Compliant Bistable Gripper
Introduction
This project focused on developing a bistable gripper that utilizes a snap-through mechanism for grasping objects without motors. The objective was to transition from thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) to spring steel to enhance reliability and predictability.
Challenges & Design Considerations
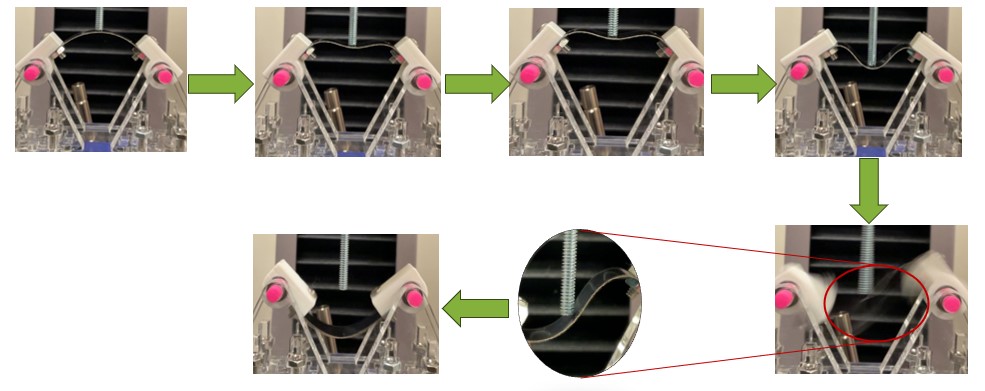
The gripper's function relies on bistability—allowing it to switch between two stable states through mechanical force alone. Key challenges included optimizing the snap-through mechanism and ensuring compact yet efficient operation. The transition to spring steel required careful adjustments to balance flexibility, durability, and performance.
My Contributions
My role centered on solving a beam buckling partial differential equation (PDE) using advanced numerical methods, followed by mechanical testing to validate the theoretical predictions. Specific contributions included:
- Mathematical Modeling: Developed equations to simulate beam buckling behavior.
- Material Analysis: Evaluated spring steel properties for optimal performance.
- Experimental Testing: Conducted deflection and force analysis for design validation.
Findings & Results
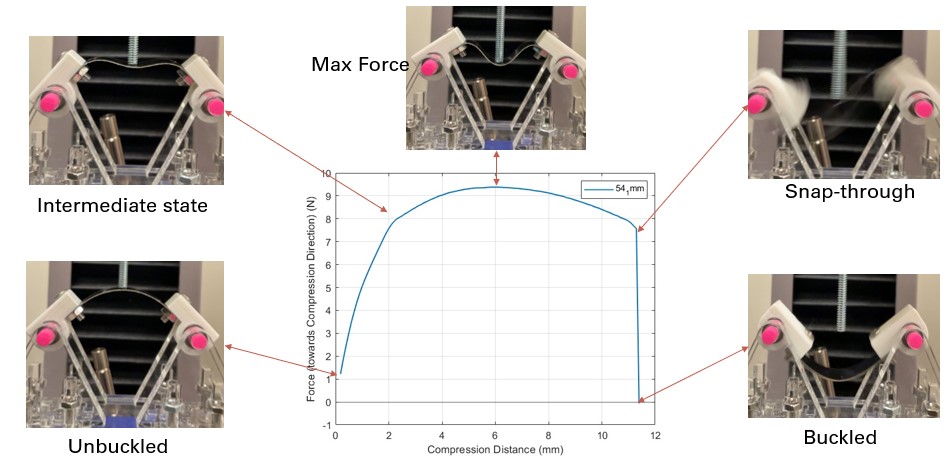
Simulation results highlighted the importance of precise actuation point placement for reliable bistability. By adjusting this parameter, we significantly improved the gripper’s performance compared to TPU-based designs.
Tests demonstrated that the spring steel gripper maintained consistency across multiple conditions, making it suitable for high-speed robotic applications.
Key Takeaways
This project underscored the critical role of precise force modeling in bistable mechanisms. While the design improvements were substantial, further refinement of snap-through force calculations could enhance long-term reliability.